Malnutrition Care Score for IQR
The Malnutrition Care Score quality measure is available for 2025 hospital reporting.
The Malnutrition Care Score quality measure is available for 2025 hospital reporting.
The toolkit is a collection of evidence-based malnutrition care best practices and resources and is intended for use by all members of the care team (e.g., nurses, dietitians, physicians, patients and caregivers) who engage in care for adult patients who are malnourished or at risk of malnutrition. By using this toolkit to support quality improvement (QI), healthcare institutions may be able to:
The MQii toolkit was tested over a three-month implementation period in 2016 through a multi-site Demonstration and Learning Collaborative. The toolkit’s use demonstrated that the introduction of recommended malnutrition quality improvement actions helps healthcare institutions achieve performance goals in nutrition care. Please note that while the toolkit was tested specifically for patients ages 65+, the recommendations in the toolkit are applicable to all adults.
The MQii and its toolkit are designed to drive improvement in the clinical workflow processes and structures supporting optimal malnutrition care. The Global Malnutrition Composite Score electronic clinical quality measure (eCQM) was developed and tested as a mechanism to quantify the success of improvement actions by measuring the rates of malnutrition screening, assessment, diagnosis, and care planning. While these same care processes are measured by the GMCS, capture of data and calculation of GMCS results requires an additional complementary workstream of EHR design optimization. To ensure the GMCS performance rate accurately reflects the care being delivered, hospitals will need to take steps to ensure their EHR is up-to-date and designed to capture the necessary data elements in a structured manner using the GMCS-defined value sets. Learn more about the GMCS and technical requirements from the Commission on Dietetic Registration’s GMCS site.
The MQii toolkit provides practical resources to help healthcare institutions deliver optimal nutrition care
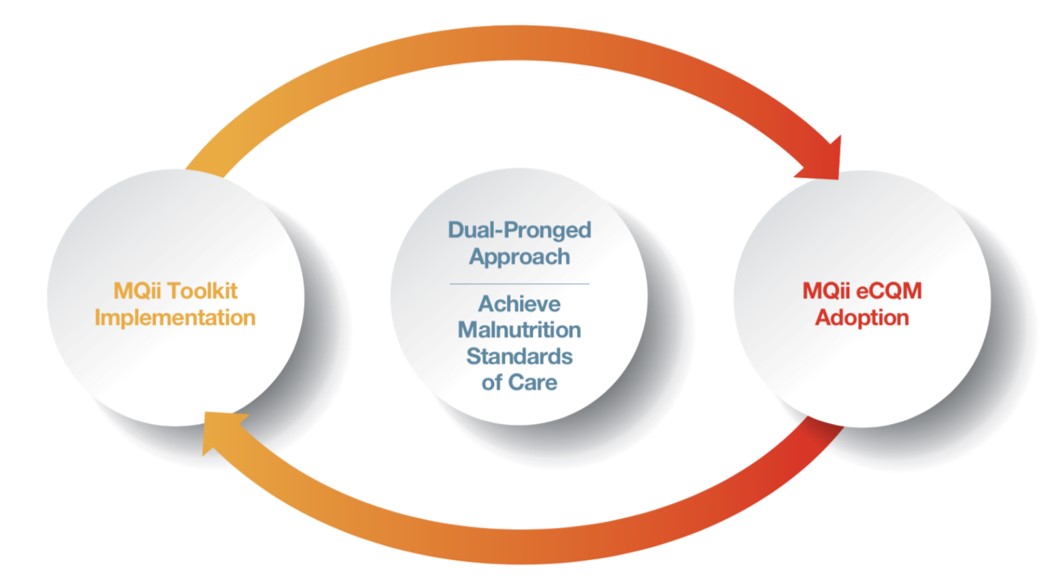
GMCS performance results will help healthcare institutions demonstrate their success in meeting the standards of care
Malnutrition is defined as the inadequate intake of protein and/or energy over prolonged periods of time and can include under- and over-nutrition. Malnutrition results in loss of fat stores and/or muscle wasting including starvation-related malnutrition, chronic disease-related malnutrition, and acute disease or injury-related malnutrition.[3]
Evidence suggests that 20 to 50 percent of patients are at risk for malnutrition or are already malnourished at the time of hospital admission,[4] but only 8 percent receive a diagnosis of malnutrition – meaning many patients may be going unrecognized and untreated.[5] The inability to identify and diagnose these patients leaves them at risk for other medical complications.
Despite the evidence that demonstrates the benefits of nutrition for healing and recovery, and a clinical consensus model for implementing optimal malnutrition care, significant performance gaps remain in hospitals with respect to malnutrition screening, assessment, intervention, monitoring, and overall care. Depending on the level of malnutrition awareness in your facility, you may want to build support by sharing information regarding the burden and impact of malnutrition and how addressing it can improve patient and hospital outcomes. Case studies and supporting evidence can be found in the Quality Improvement section of the MQii website.
Click the drop down sections below to review and access major sections of the MQii Toolkit:
This section includes:
This section includes:
This section includes:
This section includes:
This section includes:
This section includes:
See the glossary here.
See the References here.
This section includes:
Visit the Resource Repository to access turnkey resources mentioned throughout the MQii Toolkit, and more.
On this page:
MQii Toolkit:
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |

Members Area